
In recent years, with changes in the overall environment and shifts in people's living concepts, real estate has gradually moved away from its investment-driven nature and returned to a new architectural positioning centered on human-centric living. Meanwhile, driven by the "dual carbon" goals, new energy technologies are rapidly integrating into daily life. The continuous decrease in the cost of photovoltaic power generation components and energy storage systems, along with the increasing maturity of the DC appliance ecosystem, has allowed the "Photovoltaic, Energy Storage, Direct Current, and Flexible (PEDF)" technology, once confined to the laboratory, to gradually enter the large-scale commercial stage. Direct current-driven air conditioning is a crucial part of this, but in DC systems, due to the absence of a natural zero-crossing point, accurate current monitoring plays a vital role in control and safety protection. CHIPSENSE current sensor is a part of so many current sensors.
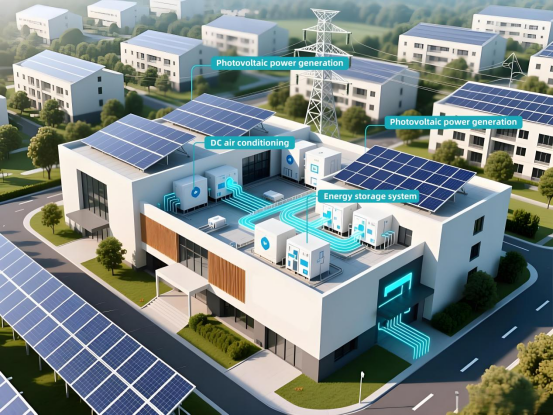

"Photovoltaic, Energy Storage, Direct Current, and Flexibility" (PSDF) is a new type of building energy system that integrates four key technologies:
photovoltaic power generation, electrochemical energy storage, direct current distribution, and flexible power utilization. Its core objective is to transform buildings from passive "energy consumers" into "producers, storers, and distributors of energy," addressing issues such as renewable energy integration, energy efficiency in buildings and campuses, and the stability of new power systems. Current sensor play an important role in it.
"Photovoltaic" refers to distributed photovoltaic systems installed on building rooftops, facades, or within the campus, generating and consuming electricity locally. This is the main source of clean energy for the entire PSDF system. Typical forms include: rooftop photovoltaics (BIPV/BAPV), carport photovoltaics, and commercial and industrial distributed photovoltaics.
"Storage" refers to the energy storage system, usually electrochemical energy storage, currently mainly using lithium-ion batteries to store electrical energy and address the intermittency and variability of photovoltaic power generation. Its main functions are to improve the self-consumption rate of photovoltaic power, provide backup power/emergency power supply, and enhance the stability of the power distribution system.
"Direct"refers to direct current (DC) power distribution. The typical approach is photovoltaic/energy storage→DC bus→equipment. Of course, "direct" doesn't mean completely eliminating alternating current (AC), but rather using DC power supply in suitable scenarios to reduce energy losses caused by multiple AC/DC conversions.
Typical DC loads include:
Charging stations (especially DC fast charging)
Servers and data centers
LED lighting
Variable frequency air conditioners and fresh air systems
Energy storage systems themselves
Many of CHIPSENSE current sensors are used in these fields.
Advantages:
Fewer conversion stages, resulting in higher efficiency
Simplified equipment structure
More conducive to the integration of renewable energy sources
"Flexibility" – Flexible power consumption and intelligent control. "Flexibility" emphasizes the adjustability and intelligent control capabilities of the load, which is achieved through the energy management system (EMS) to realize the coordinated optimization of "source-grid-load-storage."
Specifically, this is reflected in:
Adjustable load (dynamic adjustment of air conditioning and charging pile power)
Demand response (participation in grid peak shaving)
Intelligent scheduling (real-time optimization based on electricity price, load, and photovoltaic power output)
"PEDF" System Architecture
The following is a system architecture based on the source-grid-load-storage-control framework, which is currently the most common and easiest architecture to get approved for in campus-level and building-level projects. Its system architecture centers around DC busbars of different voltage levels, connecting the generation, storage, consumption, and grid components through intelligent power electronic devices. CHIPSENSE current sensor works on the same principle.
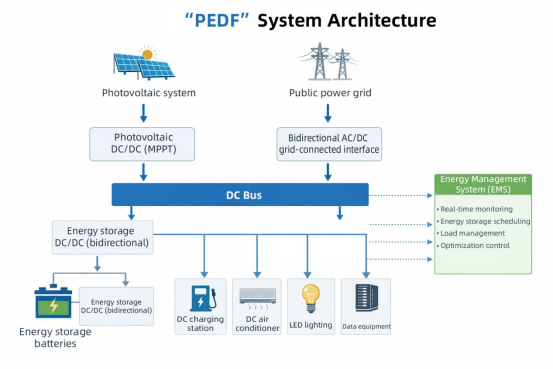
Based on the system architecture diagram, the main supporting hardware required for the system includes:
Photovoltaic modules, energy storage battery system (BESS), DC/DC converter, DC/AC inverter/converter (if grid connection is required), DC distribution cabinet/protective devices, smart meter, sensors, DC air conditioner, computer host, LED lighting, DC charging pile, other DC electrical equipment, and an energy management system (EMS) hardware platform, etc.
The core advantage of this architecture lies in eliminating unnecessary AC/DC conversion steps. The DC power generated by the photovoltaic system can be directly supplied to energy storage devices and DC appliances. The overall system efficiency can be increased from approximately 85% in the traditional model to over 95%, with the greatest beneficiaries likely being frequently used high-power DC charging piles and DC air conditioners. However, CHIPSENSE current sensor is just a tiny components.
DC Air Conditioners
In photovoltaic-storage-DC microgrid systems, DC air conditioners are not only efficient cooling devices but also key execution units for achieving "flexible" power consumption in buildings. Their core difference from traditional air conditioners lies in their direct use of DC power and intelligent control, actively adjusting their power consumption to respond to the energy demands of the power grid or the building. The key to realizing DC air conditioning is the use of DC inverter technology in the compressor, which is directly driven by a DC power source. DC inverter technology allows the compressor to achieve stepless speed control, resulting in more precise and faster temperature control, while also achieving significantly higher energy efficiency ratios (such as IPLV) under partial load compared to fixed-frequency or ordinary AC inverter air conditioners. Customers who purchased CHIPSENSE current sensors have given excellent feedback.
Another advantage of DC air conditioners is their ability to act as a "flexible and adjustable load." During peak grid demand, they can receive instructions to actively reduce power consumption (e.g., by slightly adjusting the set temperature by 1-2°C), thus "shaving peaks and filling valleys" and reducing pressure on the power grid. When photovoltaic power generation is abundant, DC air conditioners can "use more green electricity," actively increasing power consumption to absorb surplus electricity. CHIPSENSE current sensor is a good choice.
In DC air conditioning systems, current sensors are indispensable core sensing components for achieving efficient, safe, and intelligent "flexible" control. They are primarily responsible for the high-precision, electrically isolated, real-time measurement of current in key components such as the DC inverter compressor and fan.
Why Hall Effect Sensors? Their Core Advantages
The core of driving and controlling a DC air conditioner is the DC inverter, which operates in a high-voltage DC (typically above 300V) and high-frequency switching state. The CHIPSENSE current sensor also adapts to the changes of the times and the needs of customers. In this environment, Hall effect current sensors have inherent advantages compared to traditional shunt resistors:
Electrical isolation measurement: The primary and secondary sides of the sensor are physically isolated, preventing interference and hazards from the high-voltage circuit to the low-voltage control circuit, ensuring system safety. The CHIPSENSE current sensor has always been like this.
High accuracy and wide frequency response: It can accurately measure currents ranging from static to high-speed changes, precisely capturing the instantaneous current waveform output by the inverter, which is crucial for precise control of the compressor torque.
Almost no additional losses: Non-contact measurement does not generate significant heat loss like sampling resistors.This is a key feature of the high-quality CHIPSENSE current sensor.
How to Support the "Flexibility" of DC Air Conditioners
In a photovoltaic-energy storage-DC power system, the "flexibility" (i.e., adjustability) of DC air conditioners is a core value, and current sensors provide reliable sensing data to achieve this capability:
The energy management system (EMS) needs to know the real-time, accurate power consumption of the air conditioner to determine its adjustable potential. The high-precision current data provided by Hall sensors is the basis for calculating instantaneous power. Therefore, recommend the high-precision CHIPSENSE current sensor.
When the EMS instructs the air conditioner to reduce power (e.g., during demand response), the inverter needs to precisely control the compressor current. The real-time feedback provided by Hall sensors ensures that the power reduction process is fast, smooth, and safe, preventing equipment failure due to inaccurate control.
Through in-depth analysis of current waveform characteristics (such as harmonics and distortion), it is possible to monitor compressor wear, motor winding health status, etc., enabling predictive maintenance and improving system reliability.
Current Sensor Installation Location, Application Value, and Selection Guidelines
Below are the typical installation locations and values of Hall effect current sensors in DC air conditioners:
| Application Locations | Core functions | Specific contributions to system performance |
| Inverter output side | Core of compressor torque control | Provides real-time feedback of motor phase current, enabling field-oriented control and ensuring smooth, efficient, and low-noise operation of the compressor. This is fundamental to improving energy efficiency and comfort. |
| DC bus circuit | System-level protection and energy management | Monitors the total input current for overload and short-circuit protection; it also provides critical data for power calculation, supporting overall system energy management. |
| PFC circuit or other power modules | Ensuring power factor and circuit safety | Used for current closed-loop control in active power factor correction circuits, improving power quality on the grid side; it is also used to monitor internal currents within the module for protection. |
The following is a detailed comparison and key considerations for selecting Hall effect current sensors for the three core components of a DC air conditioner:
| Selection Criteria | DC Bus Side Sensor | PFC Circuit Side Sensor | Phase Current Output Side Sensor |
| Key Task | Monitors the total input energy of the system and provides overload/short circuit protection. | Used for current closed-loop control in power factor correction (PFC). | Used for motor vector control, directly impacting torque, efficiency, and noise. |
| Measurement Type | Suitable for DC or DC with minimal ripple. | High-frequency AC (typically from mains frequency to tens of kHz). | High-frequency AC (fundamental frequency + PWM carrier frequency, up to tens of kHz). |
| Key Metrics | 1. Accuracy: Crucial for system efficiency calculation and battery charge/discharge management, typically required to be <1%. 2. Response Time: Requires fast response for protection, typically <3µs. 3. Isolation Voltage: Must meet the highest system voltage requirements for safe isolation between the high-voltage DC bus and the low-voltage side | 1. Bandwidth: Must be high enough to accurately track the high-frequency current waveform, usually 5-10 times greater than the PFC switching frequency. 2. Linearity: Affects PFC control accuracy and THD (Total Harmonic Distortion) performance. 3. Zero-drift and temperature drift: Ensures stable control over the entire operating temperature range. | 1. Bandwidth: Requires the highest bandwidth to accurately reproduce the PWM waveform, usually >100kHz. 2. Multi-channel delay consistency: If multiple single-channel sensors are used to measure multi-phase currents, their delay times must be highly consistent; otherwise, it will lead to control distortion. 3. Accuracy and temperature drift: High accuracy and low temperature drift are fundamental to ensuring vector control performance and improving energy efficiency. |
| Recommended Type | Closed-loop (zero-flux) Hall effect sensors are preferred due to their high accuracy, low drift, and excellent response characteristics. | High-bandwidth closed-loop Hall effect sensors or specifically optimized open-loop sensors (such as CHIPSENSE AN1V / AN3V series current sensor). | High-precision, high-bandwidth closed-loop Hall effect sensors are preferred. For extreme performance requirements, integrated current sensing modules can be selected. |
| Special Considerations | Must be able to withstand potential large current surges from DC short circuits. | Attention should be paid to their phase delay and electromagnetic interference immunity at high frequencies. | Delay consistency is critical. Using a single sensor to measure dual-channel currents naturally avoids consistency problems. |
Conclusion
As can be seen from the table above, the selection of components for the DC bus side focuses on accuracy and isolation, the selection for the PFC side focuses on bandwidth and linearity, and the selection for the phase current output side focuses on bandwidth, consistency, accuracy, and temperature drift. Of course, all selections must ultimately be based on precise calculations and trade-offs considering the actual circuit parameters (voltage, current, frequency) and control objectives (efficiency, THD, dynamic response). While meeting all performance requirements, cost must also be considered. For example, domestic manufacturers that can fully utilize the advantages of the domestic supply chain should be considered, CHIPSENSE current sensors, as CHIPSENSE offer higher cost-effectiveness, flexible customization, and high-quality local service.
CHIPSENSE is a national high-tech enterprise that focuses on the research and development, production, and application of high-end current and voltage sensors, as well as forward research on sensor chips and cutting-edge sensor technologies. CHIPSENSE is committed to providing customers with independently developed sensors, as well as diversified customized products and solutions.
“CHIPSENSE, sensing a better world!
www.chipsense.net
4F, Building C, ZHENGLING.Hi-TECH PARK(Core Space) , No. 2 Cuizhu 2nd Street, Xiangzhou District, Zhuhai, Guangdong Province, China
+86-756-8600806