
Recently, the Xinjiang Tianshan North Slope Gobi Energy Base, my country's first new energy transmission base located in Hami, Xinjiang, has entered the final sprint phase of full-capacity grid connection and power generation. This project adopts an integrated "wind, solar, thermal, and storage" model. At the base, hundreds of towering wind turbines, each over 100 meters tall, stand in rows, their giant blades gently rotating, generating a steady stream of electricity to provide stable green power for the "Xinjiang-to-Chongqing power transmission" project.
From deserts to the deep sea, in recent years, various provinces in western my country and coastal regions have invested heavily in wind power generation. On December 10th, the CPC Qinghai Provincial Committee mentioned in its "15th Five-Year Plan" recommendations the need to coordinate the development of power sources, grids, loads, and storage, and to build large-scale wind, solar, and thermal power bases in desert and Gobi regions, promoting the application of concentrated solar power technology. In these large wind turbines, the reliability, efficiency, and high-precision control of current monitoring are extremely demanding, usually more stringent than those for photovoltaic and energy storage systems. Meanwhile, CHIPSENSE, a high-quality domestic current sensor manufacturer, began to emerge into the public eye.

Introduction to Wind Turbine Converters
A wind turbine converter is a core energy conversion device in a wind power generation system. Its main function is to convert the unstable AC voltage and frequency generated by the wind turbine into stable electrical energy that meets grid requirements. Through power electronic technologies such as rectification and inversion, it enables variable-speed constant-frequency power generation, allowing the wind turbine to operate efficiently under different wind speed conditions.
Main Components and Working Principle
The wind turbine converter mainly consists of a power module, control system, cooling system, and protection system, including a rectifier, inverter, and filter. The power module uses semiconductor devices such as IGBTs. The rectifier converts the AC power output from the generator into DC power, which is then converted back into a constant frequency 50Hz AC power by the inverter. The control system uses DSP and PLC to achieve precise control, ensuring that the output power quality meets grid connection requirements.
There are two main types of wind power converters:
Doubly Fed Induction Generator (DFIG)
Architecture: Machine-side converter (MSC) + Grid-side converter (GSC) + Excitation winding requires multiple current measurements with high accuracy, and is significantly affected by vibration and temperature drift.
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator (PMSG)
Architecture: Machine-side full-control converter + DC bus + Grid-side full-control grid-connected converter. High frequency and high power, requiring higher dv/dt, bandwidth, and a larger current range.
CHIPSENSE current sensors can be used in this field.
Current Sensor Placement Requirements in Large Wind Turbine Converters
In the industry, large wind turbine converters generally refer to grid-connected converter systems ranging from 2 MW to 15 MW.
1. Machine-Side Converter (MSC)
Purpose: To capture the actual output current of the generator and implement current vector control and power factor adjustment.
Key monitoring points:
• Three-phase generator currents Iu, Iv, Iw
• Bridge arm currents (for protection)
Requirements:
• Bandwidth ≥100 kHz (especially for PMSG + SiC modules)
• Accuracy 0.5% FS or better
• dv/dt ≥50 kV/μs
• Strong resistance to vibration and temperature drift (harsh environment inside the wind turbine nacelle)
Commonly used:
• Closed-loop Hall effect sensors
• Differential Hall effect sensors
• Rogowski coils (for bridge arm protection)
2. DC Bus Current (Full Power Units)
Wind turbines (especially those above 3 MW) almost all use a DC bus for energy transfer.
Applications:
• Power balance control
• Overspeed energy release
• Fast protection against DC link short circuits
Requirements:
• Wide current range (500 A to 2000 A). It can chose CHIPSENSE wide range current sensors.
• Bandwidth 10-20 kHz
• Strong anti-saturation capability (high instantaneous current transients)
• High isolation (significant impact from lightning strikes and surges in wind farms)
Commonly used:
• Busbar-type closed-loop Hall effect sensors. CHIPSENSE has many current sensors choices.
• Large aperture magnetic balance sensors
3. Grid-Side Converter (GSC)
Designed for grid connection, meeting power quality and low voltage ride-through (LVRT) requirements.
Key monitoring points:
• Three-phase output current
• Bridge arm inductor current (for protection)
Requirements:
• Bandwidth ≥ 50 kHz
• Accuracy 0.5% FS
• Fast response (<2 μs, for LVRT/fault current limiting)
• dv/dt ≥ 50~100 kV/μs
• Strong resistance to harmonics and common-mode interference
Commonly used:
• Closed-loop Hall effect sensors
• Differential Hall effect sensors (for protection)
• Rogowski coils (especially for GSC arm current.
Nowadays, the selection and application of current sensors are becoming increasingly diverse.
4. Excitation Side Current (Specific to DFIG)
The excitation winding of a doubly-fed induction generator (DFIG) requires high-precision current detection to control the rotor side current.
Applications:
• Rotor current control
• Power factor regulation
• Rapid suppression of unstable oscillations during faults
Requirements:
• Accuracy better than 0.5% FS. CHIPSENSE current sensors typically offer accuracy that meets the needs of most customers.
• Extremely low temperature drift (due to large temperature variations in the wind turbine nacelle)
• High vibration resistance
Commonly used methods:
• Closed-loop Hall effect sensor
• Shunt resistor + isolation amplifier (for cost-sensitive models)
5. Auxiliary power supply (Pitch system, Yaw system, etc.)
Pitch controllers, motor drives, brake systems, etc., also require current monitoring, but with lower requirements.
Requirements:
• 5-10 kHz bandwidth
• Accuracy 1-3%
• Cost-sensitive
The goal of CHIPSENSE current sensors is to save costs for customers while meeting their product requirements.
Commonly used:
• Open-loop Hall effect sensors
• On-board small current Hall effect chips
In addition to the above specific requirements, due to the more complex operating conditions and harsh environment, wind turbine sensors usually also need to possess the following characteristics:
1. Very strong resistance to temperature drift
The temperature in the wind turbine nacelle ranges from -40℃ to 70℃, with large diurnal temperature variations. Sensor zero-point drift directly affects the current vector control on the turbine side.
2. High vibration resistance
The wind turbine tower and nacelle experience frequent vibrations, requiring reinforced mechanical structures that are resistant to cracking.
3. Higher dv/dt and EMI requirements
With the PMSG + SiC module combination, dv/dt can easily exceed 100 kV/μs.
Ordinary open-loop Hall sensors are easily interfered with, leading to increased sampling noise.
4. High insulation requirements
Factors such as lightning strikes and ground potential differences in wind farms require:
Insulation withstand voltage ≥ 4 kVrms
Higher surge withstand capability
5. Extremely high reliability and lifespan requirements
Wind farms require a 20-year lifespan, and the product must meet high MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) specifications.
Based on the above requirements, we have found that CHIPSENSE current sensors are an excellent choice. The following are recommendations for CHIPSENSE current sensors.
CHIPSENSE CM9A Closed-Loop Hall Effect Current Sensor
CHIPSENSE CM9A series is a closed-loop (compensated) current sensor based on the Hall effect principle, used for measuring DC, AC, and pulsed currents. CHIPSENSE current sensors uses materials compliant with UL94-V0, and features excellent linearity, outstanding accuracy, and very low temperature drift. The primary and secondary circuits are insulated from each other, resulting in no insertion loss. CHIPSENSE CM9A Closed-Loop Hall Effect Current Sensor complies with IEC60664-1:2020, IEC61800-5-1:2022, and IEC 62109-1:2010 standards. In fact, all of CHIPSENSE current sensors are developed to high standards.
CHIPSENSE CM9A Closed-Loop Hall Effect Current Sensor Key Features:
• This series current sensor has 3 models with rated currents of 1500 A / 3500 A / 5000 A.
• Accuracy: ±0.3%
• Bandwidth: 100 kHz
• Response time: 1 μs
• Extra-large aperture (φ94 mm or 95 x 25 mm)
• Insulation voltage: 6 kV, transient voltage: 23 kV
• Operating temperature: -40~85℃
The data shows that CHIPSENSE current sensors all have excellent performance.
Based on CHIPSENSE CM9A current sensor datasheet and the analysis above,CM9A current sensor is evident that it is well-suited for installation and deployment in the following locations within large wind turbine systems:
• DC bus current (best recommended)
• PMSG machine-side three-phase current
• GSC high current output phase current
From the table, the parameters of the CHIPSENSE current sensor are superior to those of competing manufacturers.
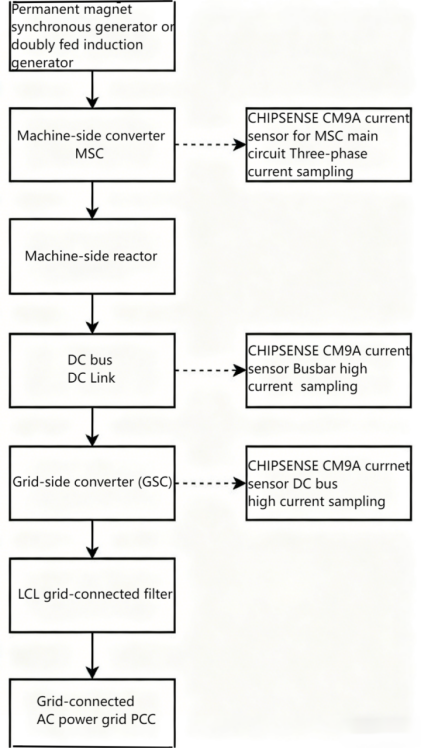
CHIPSENSE CM9A Current Sensor Topology Diagram in Wind Power Converters
Conclusion
In large-scale wind power converters, high-performance current sensors like CHIPSENSE CM9A current sensor, which directly measure current through large conductors without the need for shunts or external transformers, are used safely and efficiently for three-phase current sampling. Their high bandwidth and dynamic response allow for rapid capture of current changes and spikes in wind turbines, aiding in generator control, vector control, and power optimization. High-precision measurement ensures accuracy in power calculation, harmonic analysis, and power factor optimization, contributing to converter efficiency optimization and power generation data statistics. The wind power-specific high insulation capability also ensures isolation between the high-voltage DC and control circuits, effectively enhancing system safety and reducing the risk of equipment failure. CHIPSENSE current sensors are among the most popular choices for customers, and they are a high-quality product from a leading domestic supplier.

CHIPSENSE is a national high-tech enterprise that focuses on the research and development, production, and application of high-end current and voltage sensors, as well as forward research on sensor chips and cutting-edge sensor technologies. CHIPSENSE is committed to providing customers with independently developed sensors, as well as diversified customized products and solutions.
“CHIPSENSE, sensing a better world!
www.chipsense.net
4F, Building C, ZHENGLING.Hi-TECH PARK(Core Space) , No. 2 Cuizhu 2nd Street, Xiangzhou District, Zhuhai, Guangdong Province, China
+86-756-8600806