
The development and utilization of new energy sources is a long-term and ambitious strategic goal in my country. Under this strategic framework, my country's new energy sector has experienced rapid development in recent years, with solar energy leading the way. Besides the common photovoltaic power generation, solar energy also includes concentrated solar power (CSP). On November 18th, the Concentrated Solar Power Branch of the China Electricity Council was established. Data released at the founding meeting showed that the annual compound growth rate of my country's CSP industry reached 11.7%, more than double the global average. The establishment of the CSP branch will accelerate the standardization and engineering development of the CSP industry. Against this backdrop, choosing the appropriate current monitoring solution for CSP power plants is becoming a crucial question for power plant builders and operators. Hall effect current sensors are play an important role in it. The CHIPSENSE current sensor will serve as a typical example.

I.What is solar thermal power generation, and what are its characteristics?
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) is a clean energy technology that converts solar energy into thermal energy through concentrating techniques, and then uses this thermal energy to drive a turbine to generate electricity. Its core principle is to use mirrors or lenses to focus sunlight onto a receiver, heating a heat transfer medium (such as molten salt or thermal oil), which then produces high-temperature, high-pressure steam to drive a turbine, ultimately powering a generator to produce electricity. Currently, CHIPSENSE current sensors can also achieve this.
Unlike photovoltaics, CSP possesses inherent energy storage capabilities, allowing for long-term regulation through molten salt energy storage systems. This gives CSP power plants the following characteristics:
Continuous and stable dispatchable clean power output
Long-term energy storage capacity, typically 8–12 hours
Strong peak and valley load adjustment capabilities, capable of performing frequency regulation similar to thermal power plants
Strong resistance to extreme environments such as wind and sandstorms and high temperatures
These are all characteristics that enable CHIPSENSE current sensors to meet customer needs.
Solar thermal power plants utilize a large number of high-power, high-voltage power conversion devices in their power generation, heat storage, and heat exchange sections, making current detection a core aspect of system design.
II.What are the key current detection points in a concentrated solar power plant?
A concentrated solar power plant typically consists of a mirror field, a receiver, a thermal storage system, a steam generation system, and a power generation and grid connection side. CHIPSENSE current sensor technology is gradually improving in this area. The power electronic equipment is mainly concentrated in the following parts, and these components require current detection:
1. Solar Tracking Drive System
In a typical tower-type concentrated solar power plant, a mirror field may contain tens of thousands of heliostats. Each mirror is driven by two motors for horizontal (azimuth) and vertical (elevation) movement. Hall effect current sensors are connected in series in the motor drive circuit to monitor the armature current in real time. The current is proportional to the motor output torque (TxI). By monitoring the current waveform, the controller can achieve "torque feedback".
For example, the following control logic (pseudocode):
Python
def motor_protection_logic(current_sensor_val, wind_speed):
# current_sensor_val: The real-time current value returned by the Hall sensor. (Amps)
# RATED_CURRENT: Motor rated current
# STALL_THRESHOLD: Stall threshold (typically 1.5-2 times the rated current)
# 1. Stall/Jam Detection
if abs(current_sensor_val) > STALL_THRESHOLD:
stop_motor()
trigger_alarm("Mechanical Stall Detected")
# 2. Wind load compensation (simplified model)
# When the wind speed is high and the current fluctuates abnormally, it is determined that wind load interference is occurring, and a wind avoidance strategy is activated.(Stow Mode)
elif wind_speed > MAX_WIND_SPEED and abs(current_sensor_val) > (RATED_CURRENT * 0.8):
enter_stow_mode() # Adjust the mirror to a horizontal or safe angle.
log_event("High Wind Load Compensation Active")
# 3. Normal PID tracking control
else:
pid_control_loop(current_sensor_val)
If the current remains consistently high, it may be due to mechanical jamming or a control system malfunction, causing the mirror field to deviate from the optimal angle and affecting heat absorption efficiency.
2. Molten Salt Pumps and Hydraulic Pump Inverters
Molten salt pumps are the "heart" of concentrated solar power plants, requiring high driving power, and the inverters typically operate in the tens to hundreds of kilowatt range.
High-precision real-time detection of the pump's three-phase main current is required for overload protection and closed-loop control.
3. Thermal Energy Storage System Electric Heating Device
Some power plants are equipped with electric heating subsystems to improve deep valley filling capabilities.
Features: High current, requiring high demands on sensor range, isolation voltage resistance, and anti-interference capabilities.
4. Grid-Connected Power Conversion System (PCS)
The grid-connected side of concentrated solar power plants is usually similar to photovoltaic inverters, including a DC/AC main converter, DC bus, reactor, capacitor bank, etc.
Key monitoring points include:
DC bus current
Three-phase main circuit current
Residual current and protection current at the grid connection point
This section has the highest demands on sensor bandwidth, response speed, and insulation.
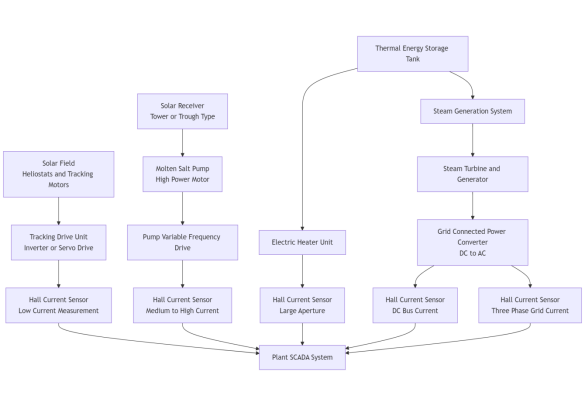
III.The Core Value of Hall Effect Current Sensors in Concentrated Solar Power Generation
As the equipment capacity of concentrated solar power plants continues to expand, system designers are upgrading from "accurate measurement" to "stable and reliable measurement." CHIPSENSE current sensor also boasts excellent performance.
Hall effect current sensors have inherent advantages in concentrated solar power applications:
1. High isolation and high insulation capabilities, suitable for high-temperature and high-voltage operating environments
Many devices in concentrated solar power plants operate at 1000 V DC or higher voltage levels.
Hall sensors measure current through magnetic isolation, without compromising the electrical isolation structure, and can withstand high insulation voltages. CHIPSENSE current sensors all feature high isolation voltage and high voltage resistance.
2. Wide temperature range to adapt to extreme working conditions
Concentrated solar power plants are often located in areas such as Qinghai, Xinjiang, and Inner Mongolia, where there are extreme temperature differences between day and night.
Enterprise-grade Hall sensors typically operate at temperatures up to -40 to 105 ℃, and industrial-grade sensors can extend to 125 ℃. Some of CHIPSENSE products can even reach higher levels.
3. Enabling high-speed, low-latency closed-loop current control
In high-power inverters and grid-connected PCS systems, controllers use high-speed PWM modulation.
The low-latency output of Hall sensors significantly improves the system's response speed and dynamic performance.
4. Easy system integration, suitable for centralized and distributed measurement
Concentrated solar power plants have a large number of distributed drive devices.
Hall sensors are small in size and flexible in installation, making them suitable for both power cabinets and distributed deployment. The same is true for CHIPSENSE current sensors.
5. Meeting long-term lifespan and reliability requirements
The design life of concentrated solar power plants is generally 25 years or more.
Hall sensors have the advantage of being non-contact and wear-free, offering superior long-term stability compared to shunt resistors and other solutions. Therefore, when customers consider domestically produced current sensors, they will first choose CHIPSENSE current sensors.
IV. Recommended Configurations for Typical Hall Current Sensors (Engineering Reference)
Based on the electrical architecture of mainstream concentrated solar power plants, the following typical configuration approaches are suggested:
| Application Scenarios | Current rating | Recommended sensor types | Requirements |
| Motor drive system tracking | 5–20A | PCB solderable open-loop Hall effect sensor | Small size, high temperature resistance |
| Molten salt pump VFD main current | 100–600A | Closed-loop Hall effect sensor or large aperture through-hole type | High accuracy, low drift, common-mode interference immunity |
| Electric heating equipment | 200–1000A | High-current Hall effect sensor, busbar type | High insulation voltage, strong interference immunity |
| PCS high-frequency inverter current | 50–800A | Closed-loop high-speed Hall effect sensor | Bandwidth in the 100 kHz range, low latency |
| DC bus current detection | 200–2000A | Large aperture Hall effect sensor (e.g., CHIPSENSE CM series) | High voltage, resistance to temperature variations |
The CHIPSENSE CM series CM5A H01 current sensor can be used as a reference.
V. Trend Analysis:Concentrated Solar Power Will Create a New Incremental Market for Sensors
Currently, my country has successfully mastered mainstream concentrated solar power technologies such as tower, trough, and Fresnel systems, with a localization rate of over 95% for technical equipment, and key materials and equipment are independently controllable. As various provinces in China begin to promote multi-energy complementary projects combining "concentrated solar power + photovoltaic" and "concentrated solar power + energy storage," it is predicted that by 2030, the global installed capacity of concentrated solar power will increase to 22.4 million kilowatts. Against this backdrop, the market demand for large-scale frequency converters and high-current PCS (Power Conversion Systems) will continue to expand. Furthermore, power plants are undergoing digital transformation, requiring more distributed monitoring points. High-precision sensors will become a critical source of fundamental data for future safety monitoring and fault diagnosis. For leading current sensor companies, their technological value in concentrated solar power generation will be further enhanced. CHIPSENSE current sensors have consistently been very popular with many customers.
CHIPSENSE is a national high-tech enterprise that focuses on the research and development, production, and application of high-end current and voltage sensors, as well as forward research on sensor chips and cutting-edge sensor technologies. CHIPSENSE is committed to providing customers with independently developed sensors, as well as diversified customized products and solutions.
“CHIPSENSE, sensing a better world!
www.chipsense.net
4F, Building C, ZHENGLING.Hi-TECH PARK(Core Space) , No. 2 Cuizhu 2nd Street, Xiangzhou District, Zhuhai, Guangdong Province, China
+86-756-8600806